Arc Welding Overview
Arc welding is a method used for joining metal objects in various industrial applications. The type of method employed for arc welding depends on the nature/quality of the material, the equipment used by the welding devices, the type of gas, and other conditions, as well as elements of the welding environment. Among these, MIG welding, MAG welding (CO2 welding), TIG welding, etc., are easy to automate by means of robots. MIG/MAG/TIG welding all focus high levels of electrical energy on the material to be welded, and the arcs and heat produced fuse the materials with wire. The materials are joined after hardening. The arcs that occur at this point will decide the form and quality of the welding area, and they can be altered under the same environmental conditions (gas composition, distance between electrodes and the basic material) by adjusting the welding voltage, current, and the speed at which wire is supplied. Skilled welding personnel will use the below welding systems to (1) use controllers to control the voltage and wire supply speed and (2) impart movement (speed and motion (torch angle, weaving motion)) to the torch with their hands to create the desired welding results.
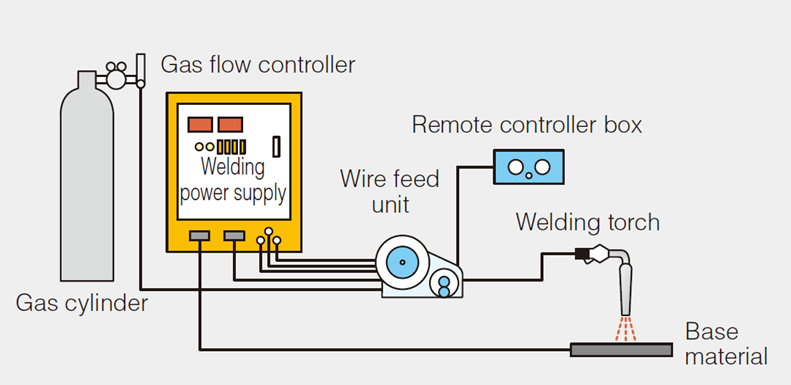
<Arc Welding System Overview>
