Understand robot motion
MANDATORY EASY 5 MIN
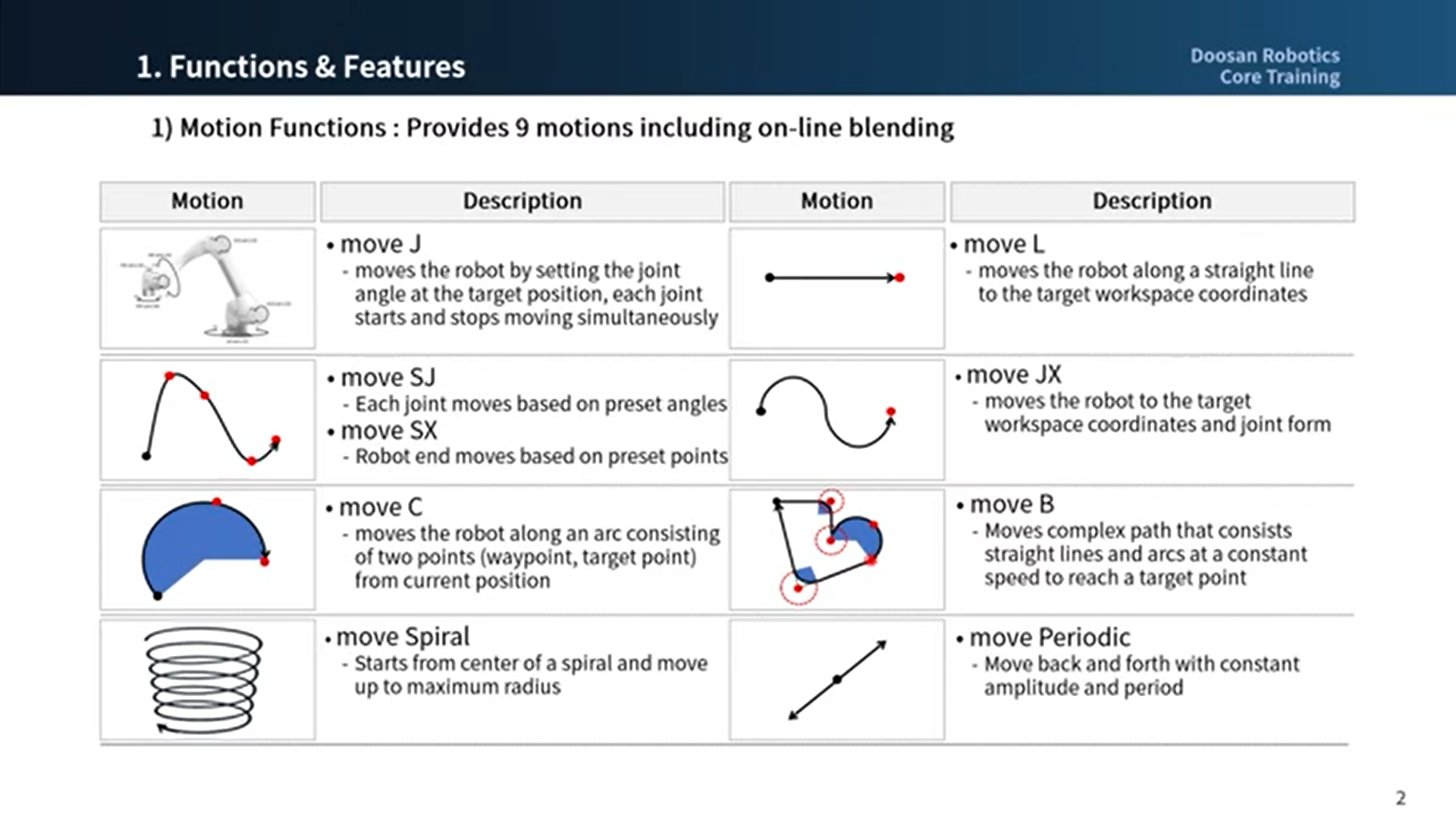
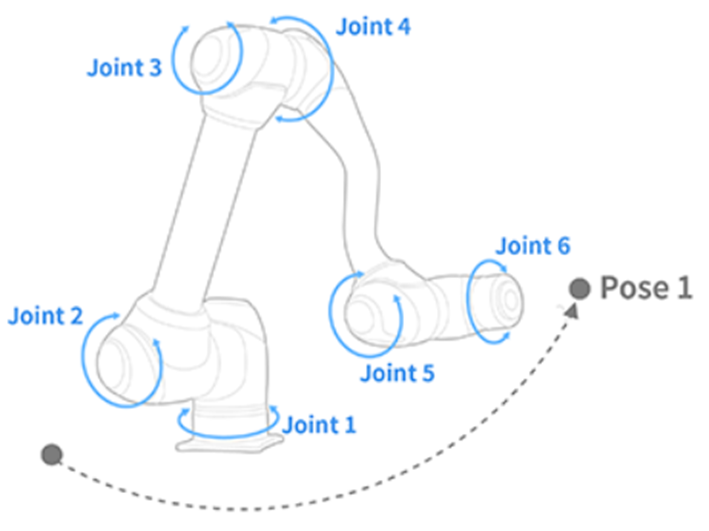
Doosan Robotics robots offer nine motions. Robot movement is controlled by standard motions, MoveJ and MoveL, and 7 motions derived from these two motions.
Types of Robot Motion
| Motion | Feature | |
|---|---|---|
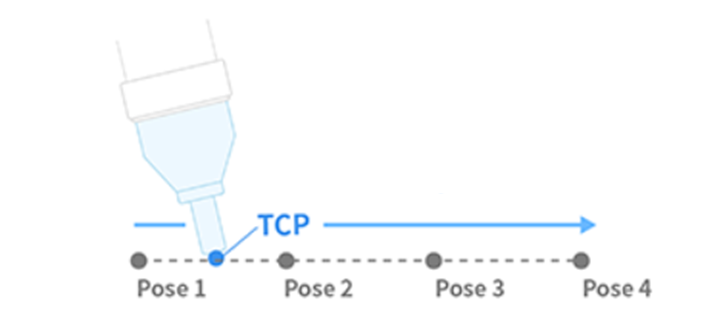
| 1 | MoveJ | Each joint of the robot moves from the current angle to the target angle and stops simultaneously
|
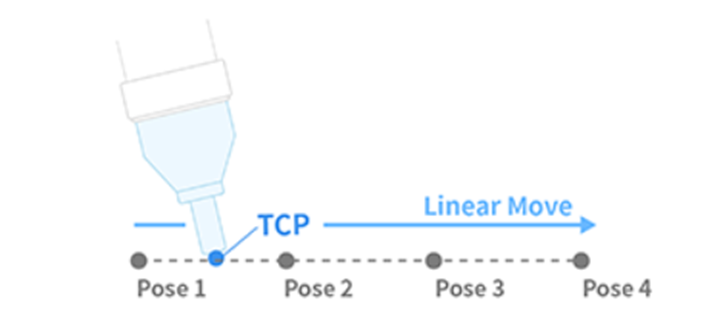
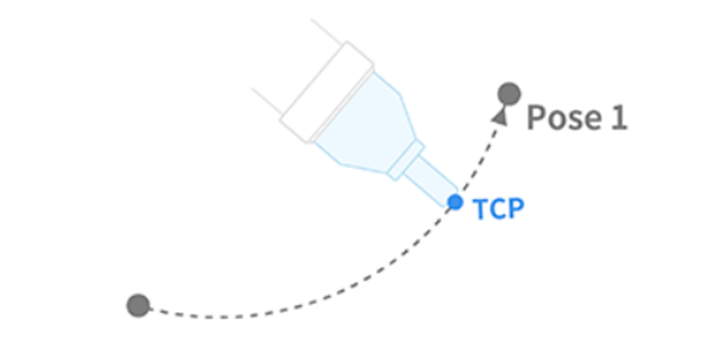
| 2 | MoveL | Robot moves to the target point while maintaining the robot TCP straight
|
| 3 | MoveSJ | Robot moves throughout all angles set by the robot
|
| 4 | MoveSX | Robot TCP moves throughout all points
|
| 5 | MoveJX | The robot pose is designated as the robot TCP moves to the target point
|
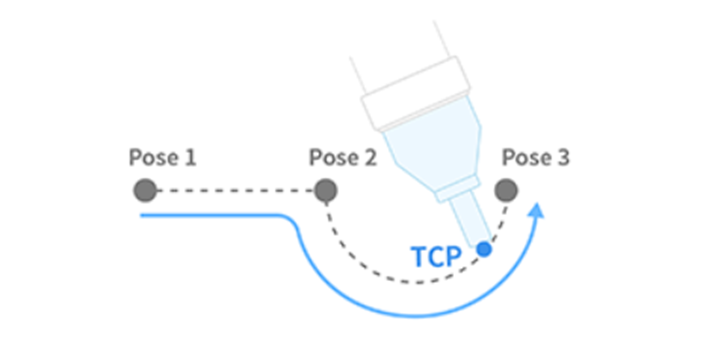
| 6 | MoveC | Robot TCP moves to target point while maintaining an arc
|
| 7 | MoveB | Robot moves to the final target point through a section consisting of continuous straight lines and arcs
|
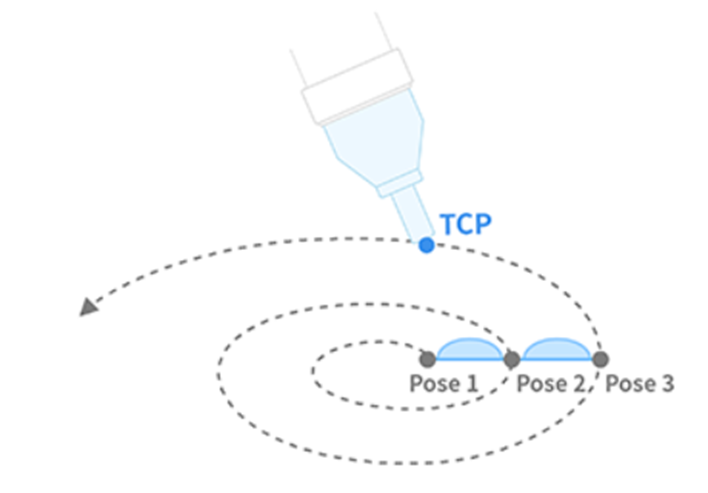
| 8 | MoveSpiral | Robot moves from the spiral center to the maximum radius
|
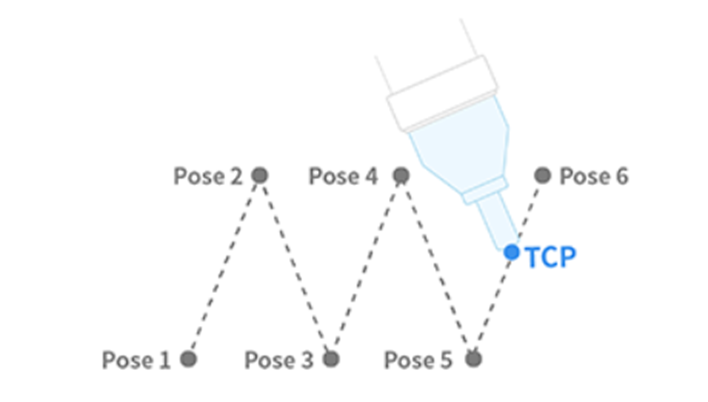
| 9 | MovePeriodic | Robot moves in a path with a constant amplitude and cycle
|
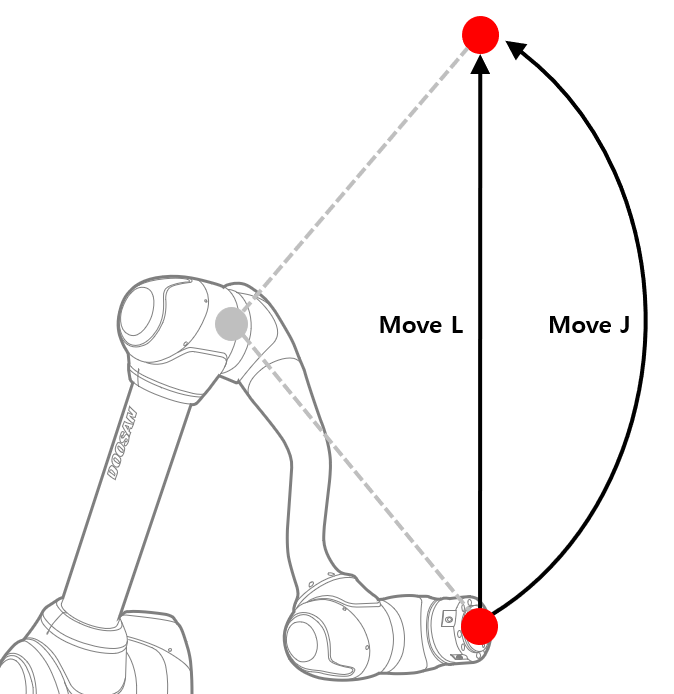
MoveJ&MoveL
Before using robot motion, it is critical to understand the standard motions MoveJ and MoveL.
- J in MoveJ refers to joints. In this motion, each joint moves to the target angle and stops simultaneously.
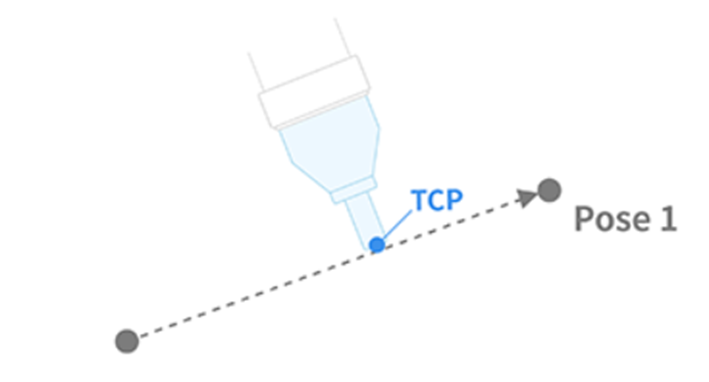
- L in MoveL refers to linear. In this motion, the TCP on the robot end moves to the target pose (position and angle) with linear motion.
| Type | MoveJ | MoveL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Move Method |
|
|
| 2 | Advantage |
|
|
| 3 | Disadvantage |
|
|
| 4 | Utilization |
|
|