CDRFLEx.amove_periodic
Features
As an asynchronous move_periodic, it operates the same as the move_periodic() function except for the asynchronous process, and executes the next line by returning as soon as motion starts without waiting for the termination of motion. A new motion command generated before the motion is terminated by move_periodic() function causes errors for security reasons. Therefore, the termination of the amove_periodic() motion must be confirmed using mwait() function between the amove_periodic() function and the following motion command before the new motion command is executed.
This command performs a cyclic motion based on the sine function of each axis (parallel and rotation) of the reference coordinate (eMoveReference) input as a relative motion that begins at the current position. The attributes of the motion on each axis are determined by amplitude and period, and the acceleration/deceleration time and the total motion time are set by the interval and repetition count.
Parameter
Parameter Name | Data Type | Default Value | Range | Description |
fAmplitude | float[6] | - | >=0 | Amplitude(motion between -fAmplitude and +fAmplitude) [mm] or [deg] |
fPeriodic | float[6] | - | >=0 | period(time for one cycle)[sec] |
fAccelTime | float | - | >=0 | Acc-, dec- time [sec] |
nRepeat | unsigned char | - | > 0 | Repetition count |
eMoveReference | enum.MOVE_REFERENCE | MOVE_REFERENCE_TOOL | - | Refer to the Definition of Constant and Enumeration Type |
Note
- fAmplitude refers to the amplitude. The input is a list of six elements that are the amp values for the axes (x, y, z, rx, ry, and rz). However, the amp input on the axis that does not have a periodic motion must be 0.
- fPeriodic refers to the time needed to complete a motion in the direction, and the input is a list of six elements that are the amp values for the axes (x, y, z, rx, ry, and rz).
- fAccelTime refers to the acceleration and deceleration time at the beginning and end of the periodic motion. The largest of the inputted acceleration/deceleration times and maximum period*1/4 is applied. An error is generated when the inputted acceleration/deceleration time exceeds 1/2 of the total motion time.
- nRepeat refers to the number of repetitions of the axis (reference axis) that has the largest period value and determines the total motion time. The number of repetitions for each of the remaining axes is determined automatically according to the motion time.
- If the motion terminates normally, the motions for the remaining axes can be terminated before the reference axis's motion terminates so that the end position matches the starting position. If the motions of all axes are not terminated at the same time, the deceleration section will deviate from the previous path. Refer to the following image for more information.
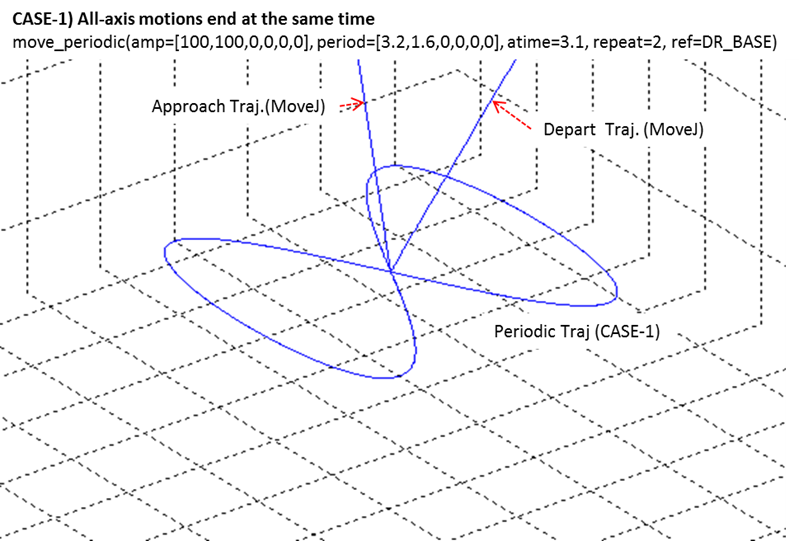
- eMoveReference refers to the reference coordinate system of the repeated motion.
- If a maximum velocity error is generated during a motion, adjust the amplification and period using the following formula.
velocity=Amplification(fAmplitude)*2*pi(3.14)/Period(fPeriodic)
(i,e., Max. velocity=62.83 mm/sec if amp=10 mm, period=1) - This function does not support online blending of previous and subsequent motions.
Return
Value | Description |
0 | Error |
1 | Success |
Example
// Repeats the x-axis (10 mm amp and 1 sec. period) motion and y rotating axis (0.5 deg amp and 1 sec. period) motion in the tool coordinate system
// 5 times.
// SET(1) the Digital_Output channel no. 1, 1 second after the periodic motion begins.
float fAmplitude[NUM_TASK] = {10, 0, 0, 0, 0.5, 0};
float fPeriod[NUM_TASK] = { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1};
Drfl.amove_periodic(fAmplitude, fPeriod, 0.5, 5, MOVE_REFERENCE_TOOL);
Sleep(1000);
Drfl.set_digital_output(GPIO_CTRLBOX_DIGITAL_INDEX_1, 1);
Drfl.mwait();
